- Maltotriose LookChem
- Robayo-Torres C et al, 2006, Maltotriose Brake: Alpha-Amylase Hydrolysis Product Maltotriose Regulates Maltase-Glucoamylase Activity and Controls Total Rates of Starch Digestion to Glucose US Department of Agriculture
- Jones BJ et al, 1983, Glucose absorption from starch hydrolysates in the human jejunum Gut
- Processing of starch Amano Enzyme Inc
- Dietvorst J et al, 2005, Maltotriose utilization in lager yeast strains: MTT1 encodes a maltotriose transporter Wiley Online Library
- Acton A, 2013 Edition Sugar Acids—Advances in Research and Application: 2013 Edition
Maltotriose
What is maltotriose?
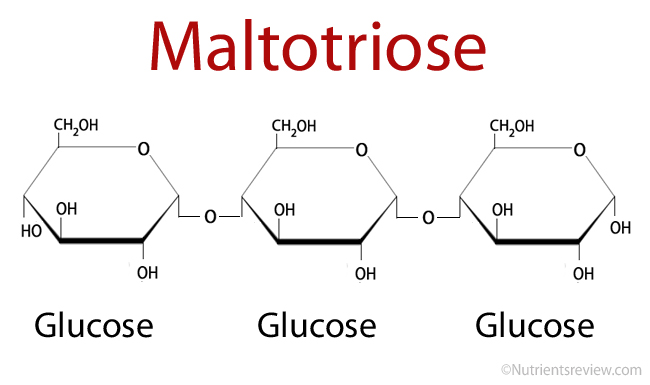
Maltotriose is an oligosaccharide, a digestible carbohydrate, composed of 3 glucose molecules linked with alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds [1].
Maltotriose Formula
Picture 1. Maltotriose structural formula
Nutrition Facts:
- Calories per gram = ~4
- Glycemic index (GI) = probably >100 [3]
- Sweetness, related to sucrose = 30% [4]
- Net carbs = 100%
Maltotriose Source and Digestion
Maltotriose is produced during digestion of starch in the mouth and small intestine by the help of the salivary and pancreatic enzyme alpha-amylase [1]. Maltotriose is broken down by the help of the small intestinal enzymes sucrase-isomaltase and maltase-glucoamylase into 3 glucose molecules, which are absorbed [2].
Maltotriose Uses
Maltotriose as a sweetener is produced from starch. It is a part of liquid glucose (a commercial sweetener composed of glucose, maltose, maltotriose and maltotetrose) and brown rice syrup. It has a water preserving ability so it can be used in breads, cakes and other baked goods [4].
Maltotriose and Cooking
Physical properties:
- A white crystalline powder [1]
- 30% as sweet as sucrose [4]
- Soluble in water [1]
- Humectant – has water preserving ability [4]
- Reducing sugar – it undergoes Maillard browning reaction [6-p.264]
- Maltotriose is a slowly fermentable sugar (being able to be broken down by yeasts). It is a part of beer wort and some of it appears in beer [5].
Related Nutrients
Carbohydrates
- Fructose
- Galactose
- Glucose
- Isomaltose
- Isomaltulose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Mannose
- Sucrose
- Tagatose
- Trehalose
- Trehalulose
- Xylose
- Erythritol
- Glycerol
- Hydrogenated starch hydrolysates (HSH)
- Inositol
- Isomalt
- Lactitol
- Maltitol
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides (IMO)
- Maltotriose
- Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS)
- Raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
- SOLUBLE FIBER:
- Acacia (arabic) gum
- Agar-agar
- Algin-alginate
- Arabynoxylan
- Beta-glucan
- Beta mannan
- Carageenan gum
- Carob or locust bean gum
- Fenugreek gum
- Galactomannans
- Gellan gum
- Glucomannan or konjac gum
- Guar gum
- Hemicellulose
- Inulin
- Karaya gum
- Pectin
- Polydextrose
- Psyllium husk mucilage
- Resistant starches
- Tara gum
- Tragacanth gum
- Xanthan gum
- INSOLUBLE FIBER:
- Cellulose
- Chitin and chitosan
- FATTY ACIDS
- Saturated
- Monounsaturated
- Polyunsaturated
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
- Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)
- Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs)
- Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs)
- Monoglycerides
- Diglycerides
- Triglycerides
- Vitamin A - Retinol and retinal
- Vitamin B1 - Thiamine
- Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin
- Vitamin B3 - Niacin
- Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid
- Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxine
- Vitamin B7 - Biotin
- Vitamin B9 - Folic acid
- Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin
- Choline
- Vitamin C - Ascorbic acid
- Vitamin D - Ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol
- Vitamin E - Tocopherol
- Vitamin K - Phylloquinone
- Curcumin
- FLAVONOIDS:
- Anthocyanidins
- Flavanols: Proanthocyanidins
- Flavanones: Hesperidin
- Flavonols: Quercetin
- Flavones: Diosmin, Luteolin
- Isoflavones: daidzein, genistein
- Caffeic acid
- Chlorogenic acid
- Lignans
- Resveratrol
- Tannins
- Tannic acid
- Alcohol chemical and physical properties
- Alcoholic beverages types (beer, wine, spirits)
- Denatured alcohol
- Alcohol absorption, metabolism, elimination
- Alcohol and body temperature
- Alcohol and the skin
- Alcohol, appetite and digestion
- Neurological effects of alcohol
- Alcohol, hormones and neurotransmitters
- Alcohol and pain
- Alcohol, blood pressure, heart disease and stroke
- Women, pregnancy, children and alcohol
- Alcohol tolerance
- Alcohol, blood glucose and diabetes
- Alcohol intolerance, allergy and headache
- Alcohol and psychological disorders
- Alcohol and vitamin, mineral and protein deficiency
- Alcohol-drug interactions