- Sugar Alcohols American Diabetes Association
- Freeman J. et al, 2004, Low-Carbohydrate” Food Facts and Fallacies Diabetes Spectrum
- Elia M et al, 2007, Energy values of macronutrients and specific carbohydrates in foods European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
- Glycerin MSDS ScienceLab
- Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers Food Standards Agency
- SCOGS (Select Committee on GRAS Substances) US Food and Drug Administration
- Glycerine (oral route) PubMedHealth
- Glycerin ChemSpider
- Glycerin specifications SRS International
- Glycerine ─ boiling and freezing points The Engineering ToolBox
- Glycerol INCHEM.org
- Goulet ED et al, 2007, A meta-analysis of the effects of glycerol-induced hyperhydration on fluid retention and endurance performance PubMed
- Glycerine Dictionary.com
- Anticaries drug products for over-the-counter human use [21CFR355.3] US Food and Drug Administration
Glycerin (Glycerol)
What is glycerin?
Glycerin is chemically a sugar alcohol [1]. On the Nutrition Facts labels, it is included in total carbohydrates, and, as a subcategory, in sugar alcohols [2]. In the EU, glycerin is listed as E number E422.
Glycerin Word Origin and Meaning
From French glycérine, from Greek glukeros = sweet [13].
Nutrition Facts:
- Calories per gram = 4.3
- Glycemic index (GI) = ?
- Sweetness, relative to sucrose = 75%
- Net carbs = probably 100%
Glycerin, Glycerine and Glycerol Are the Same
Glycerin, glycerine and glycerol are 3 names for the same substance. The name glycerin or glycerine is usually used as a product name and the name glycerol for the ingredient, for example, glycerin syrup contains 99.7 glycerol.
Glycerol vs triglycerides. Glycerol naturally occurring in foods and in the human body is usually joined with fatty acids and forms triglycerides, which are lipids, but again, glycerol as a standalone molecule is not a lipid but carbohydrate. When triglycerides are digested, they are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids, which are absorbed.
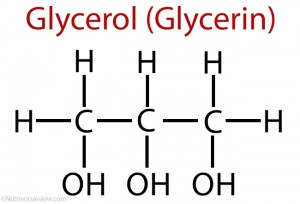
Formula
The chemical formula of glycerin (glycerol) is C3H5(OH)3.
Picture 1. Glycerol structure
Glycerin Absorption and Metabolism
Glycerin is chemically classified as a sugar alcohol, but it is more similar to sugars: it is readily absorbed and is probably converted into glucose in the human body and it provides 4.3 kilocalories of energy per gram [2,3]. Glycerin is not one of the FODMAPs (fermentable oligo-, di- and monosaccharides and polyols), because it is well absorbed in the small intestine and does not pass to the large intestine where it would be fermented by intestinal bacteria.
Glycerin is often mentioned as a sweetener with a low glycemic index, but there are no reliable sources to confirm this.
Types of Edible Glycerin
Vegetable glycerin is made from vegetable oils (palm oil, palm stearin, palm kernel oil, coconut oil, soybean oil) during production of soap or biodiesel.
Animal glycerin is a natural byproduct of animal fats (such as beef tallow) during production of soap.
Synthetic glycerin is produced from cane or corn syrup sugar, or propylene (a petroleum derivative).
Glycerin as a Food Additive
Food-grade glycerin may be added as a humectant (wetting agent), thickener, solvent or sweetener to dairy products (cream), canned goods, confections, fondant, processed fruits, jams, energy bars and other foods. The source of glycerin (animal or vegetable oil, corn syrup, petroleum) used in a food product is usually not revealed on the food labels.
Other Glycerin Uses
- An emulsifier in pills, syrups, toothpastes, mouth washes, fluoride gels, tobacco, etc.
- Anhydrous glycerin is used in fluoride gels, and is approved as an over-the-counter (OTC) anti-caries drug by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [14].
- A lubricant, enema or laxative, as a suppository is used to treat constipation.
- Oral glycerin, as a drug, is used to lower high pressure within the eye (glaucoma).
- Intravenous glycerin can be used to treat brain swelling (cerebral edema) [7].
- Glycerin may be used as a skin or hair moisturizer.
Possible Glycerin Health Benefits
In some studies, glycerin in doses about 30 mL/kg body weight slightly (by 2.6%) increased hyperhydration and endurance performance, but additional research is warranted [12].
Glycerin Safety
Glycerin as a food additive is Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [6]. Glycerin is expected to be safe to use by adults and children [7]. Glycerin has no known cancer-promoting (carcinogenic), DNA-damaging (mutagenic) or birth defect-causing (teratogenic) effects [4].
During Pregnancy
Glycerin is category C substance, which means side effects were possibly observed in animal fetuses but not in human fetuses due to lack of human studies [7].
Side Effects, Dangers
Glycerin as a sweetener used in foods does not likely cause any side effects.
Glycerin as a laxative taken by mouth can cause dry mouth, nausea, headache, diarrhea, excessive urination (polyuria) and eventual dehydration [7].
In individuals who are sensitive to palm or coconut oil, vegetable glycerin may trigger allergic reactions.
Liquid Glycerin (Syrup) and Cooking
Picture 2. Glycerin is a thick, translucent liquid
(source: Wikimedia, Creative Commons licence)
USP-grade* or food-grade glycerin syrup properties:
- A translucent, thick, viscous syrup, without odor; contains 99.7% of glycerol [8,9]
- 75% as sweet as sucrose [2]
- Highly hygroscopic – readily attracts moisture [11]
- Soluble in cold and hot water and in alcohol [4]
- Melting point = 64.4°F (18°C) [8]
- Boiling point = 554 °F (290 °C) [8,11]
* USP = US Pharmacopeia
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is glycerin vegan?
- Vegetable glycerin is usually vegan, but yeasts or bacteria may be used during the purification process.
- Synthetic glycerin is vegan.
- Animal protein is not vegan.
2. Is glycerin syrup appropriate for diabetics?
Currently, the effect of glycerin on blood glucose levels is not known; it may be similar to the effect of table sugar.
Related Nutrients
Carbohydrates
- Fructose
- Galactose
- Glucose
- Isomaltose
- Isomaltulose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Mannose
- Sucrose
- Tagatose
- Trehalose
- Trehalulose
- Xylose
- Erythritol
- Glycerol
- Hydrogenated starch hydrolysates (HSH)
- Inositol
- Isomalt
- Lactitol
- Maltitol
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides (IMO)
- Maltotriose
- Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS)
- Raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
- SOLUBLE FIBER:
- Acacia (arabic) gum
- Agar-agar
- Algin-alginate
- Arabynoxylan
- Beta-glucan
- Beta mannan
- Carageenan gum
- Carob or locust bean gum
- Fenugreek gum
- Galactomannans
- Gellan gum
- Glucomannan or konjac gum
- Guar gum
- Hemicellulose
- Inulin
- Karaya gum
- Pectin
- Polydextrose
- Psyllium husk mucilage
- Resistant starches
- Tara gum
- Tragacanth gum
- Xanthan gum
- INSOLUBLE FIBER:
- Cellulose
- Chitin and chitosan
- FATTY ACIDS
- Saturated
- Monounsaturated
- Polyunsaturated
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
- Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)
- Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs)
- Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs)
- Monoglycerides
- Diglycerides
- Triglycerides
- Vitamin A - Retinol and retinal
- Vitamin B1 - Thiamine
- Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin
- Vitamin B3 - Niacin
- Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid
- Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxine
- Vitamin B7 - Biotin
- Vitamin B9 - Folic acid
- Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin
- Choline
- Vitamin C - Ascorbic acid
- Vitamin D - Ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol
- Vitamin E - Tocopherol
- Vitamin K - Phylloquinone
- Curcumin
- FLAVONOIDS:
- Anthocyanidins
- Flavanols: Proanthocyanidins
- Flavanones: Hesperidin
- Flavonols: Quercetin
- Flavones: Diosmin, Luteolin
- Isoflavones: daidzein, genistein
- Caffeic acid
- Chlorogenic acid
- Lignans
- Resveratrol
- Tannins
- Tannic acid
- Alcohol chemical and physical properties
- Alcoholic beverages types (beer, wine, spirits)
- Denatured alcohol
- Alcohol absorption, metabolism, elimination
- Alcohol and body temperature
- Alcohol and the skin
- Alcohol, appetite and digestion
- Neurological effects of alcohol
- Alcohol, hormones and neurotransmitters
- Alcohol and pain
- Alcohol, blood pressure, heart disease and stroke
- Women, pregnancy, children and alcohol
- Alcohol tolerance
- Alcohol, blood glucose and diabetes
- Alcohol intolerance, allergy and headache
- Alcohol and psychological disorders
- Alcohol and vitamin, mineral and protein deficiency
- Alcohol-drug interactions


137 Responses to "Glycerin (Glycerol)"