- Isomaltose PubChem
- Lee HC et al, 2008, Isomaltose Production by Modification of the Fructose-Binding Site on the Basis of the Predicted Structure of Sucrose Isomerase from “Protaminobacter rubrum” PubMed Central
- PFNDAI BUlletin, May, 2006, Protein Foods and Nutrition Development Association of India
- Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency Genetics Home Reference
- Glucose-galactose malabsorption Genetics Home Reference
- Isomaltose MSDS Spectrumchemical.com
- Isomaltose Chemical Book
- Isomaltose Santa Cruz Biotechnology
- Debajyoti Das, 2012, Biochemistry, Fourteenth Edition
- de Zoeten EF et al, 2008, A 9-Month-Old Girl With Chronic Diarrhea PubMed Central
- NPCS Board of Consultants & Engineers, Handbook on Fermented Foods and Chemicals
Isomaltose
What is isomaltose?
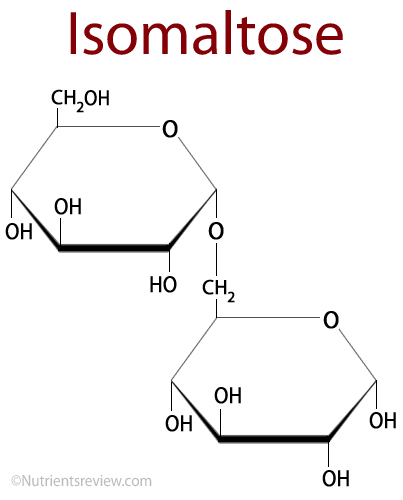
Isomaltose is a simple carbohydrate, a disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules connected with an alpha (1,6) glycosidic bond [1,2]. Isomaltose is not an essential nutrient, which means you do not need to get it from food to be healthy.
Isomaltose Formula
Picture 1. Isomaltose structural formula
Nutrition Facts for Isomaltose
- Calories per gram = ~2 [2]
- Glycemic index = “low” [3]
Isomaltose Function
Isomaltose is a source of energy – it can provide less than 2 Calories per gram, which is about half as much as sucrose [2].
Isomaltose Sources
Isomaltose probably does not naturally occur in foods in significant amounts. It appears as an intermediate product of the starch digestion.
- During caramelization of glucose, some isomaltulose is created.
- Isomaltose, which is used as a sweetener in confections, candies, processed fruits and vegetables and in canned foods, can be artificially produced:
- From sucrose by the help of the enzyme sucrose isomerase, obtained from the nonpathogenic bacterium Protaminobacter rubrum [2]
- From high maltose syrup by the help of the enzyme transglucosidase
- Corn syrup contains isomaltose, among other sugars.
Isomaltose and Dental Caries
Isomaltose has lower potential to cause tooth decay than sucrose [2].
Isomaltose Digestion
Isomaltose is digested on the surface of the small intestinal lining by the help of the enzymes isomaltase and maltase to two glucose molecules, which are then absorbed in the small intestine [9-p.412].
Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency
Individuals with a rare congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (CSID) or sucrose-isomaltose malabsorption can have reduced ability to digest isomaltose and starch (which contains isomaltose) [4]. The unabsorbed isomaltose and sucrose act as osmotic laxatives. The main symptoms are abdominal bloating, excessive gas, chronic diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, which firstly appear in infants fed with formula that contains sucrose or isomaltose [10]. Diagnosis requires small intestinal endoscopy with biopsy.
Isomaltose and Cooking
- Isomaltose is commercially available as a white crystalline powder [6,7].
- Isomaltose is hygroscopic – it attracts moisture from the air [8].
- Isomaltose is soluble in cold and hot water [6].
- Isomaltose melting point is 208.4-320 °F (98-160 °C) [6,7].
- Isomaltose is a reducing sugar [2] so it undergoes the Maillard browning reaction with amino acids.
- Isomaltose is a fermentable sugar; it can be fermented by certain strains of brewer’s yeast [11].
Similar Nutrients
- Maltose
- Isomaltulose
- Isomalt (a sugar alcohol)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides
Carbohydrates
- Fructose
- Galactose
- Glucose
- Isomaltose
- Isomaltulose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Mannose
- Sucrose
- Tagatose
- Trehalose
- Trehalulose
- Xylose
- Erythritol
- Glycerol
- Hydrogenated starch hydrolysates (HSH)
- Inositol
- Isomalt
- Lactitol
- Maltitol
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides (IMO)
- Maltotriose
- Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS)
- Raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
- SOLUBLE FIBER:
- Acacia (arabic) gum
- Agar-agar
- Algin-alginate
- Arabynoxylan
- Beta-glucan
- Beta mannan
- Carageenan gum
- Carob or locust bean gum
- Fenugreek gum
- Galactomannans
- Gellan gum
- Glucomannan or konjac gum
- Guar gum
- Hemicellulose
- Inulin
- Karaya gum
- Pectin
- Polydextrose
- Psyllium husk mucilage
- Resistant starches
- Tara gum
- Tragacanth gum
- Xanthan gum
- INSOLUBLE FIBER:
- Cellulose
- Chitin and chitosan
- FATTY ACIDS
- Saturated
- Monounsaturated
- Polyunsaturated
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
- Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)
- Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs)
- Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs)
- Monoglycerides
- Diglycerides
- Triglycerides
- Vitamin A - Retinol and retinal
- Vitamin B1 - Thiamine
- Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin
- Vitamin B3 - Niacin
- Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid
- Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxine
- Vitamin B7 - Biotin
- Vitamin B9 - Folic acid
- Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin
- Choline
- Vitamin C - Ascorbic acid
- Vitamin D - Ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol
- Vitamin E - Tocopherol
- Vitamin K - Phylloquinone
- Curcumin
- FLAVONOIDS:
- Anthocyanidins
- Flavanols: Proanthocyanidins
- Flavanones: Hesperidin
- Flavonols: Quercetin
- Flavones: Diosmin, Luteolin
- Isoflavones: daidzein, genistein
- Caffeic acid
- Chlorogenic acid
- Lignans
- Resveratrol
- Tannins
- Tannic acid
- Alcohol chemical and physical properties
- Alcoholic beverages types (beer, wine, spirits)
- Denatured alcohol
- Alcohol absorption, metabolism, elimination
- Alcohol and body temperature
- Alcohol and the skin
- Alcohol, appetite and digestion
- Neurological effects of alcohol
- Alcohol, hormones and neurotransmitters
- Alcohol and pain
- Alcohol, blood pressure, heart disease and stroke
- Women, pregnancy, children and alcohol
- Alcohol tolerance
- Alcohol, blood glucose and diabetes
- Alcohol intolerance, allergy and headache
- Alcohol and psychological disorders
- Alcohol and vitamin, mineral and protein deficiency
- Alcohol-drug interactions

2 Responses to "Isomaltose"