- Elia, M. et al, 2007, Physiological aspects of energy metabolism and gastrointestinal effects of carbohydrates European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
- Roberfroid, M., 2007, Prebiotics: the concept revisited The Journal of Nutrition
Oligosaccharides
Oligosaccharides Definition
Oligosaccharides [Greek oligo = few; sacchar = sugar] are carbohydrates composed of 3 to 9 monosaccharides.
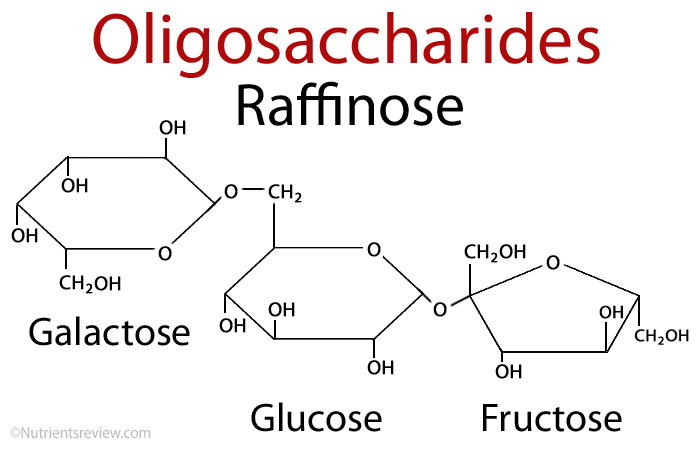
Picture 1. An oligosaccharide example: raffinose
Examples of Oligosaccharides in Foods
- Arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides (derived from cereal grains)
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) or oligofructose (Jerusalem artichokes, onions, canned foods)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS): raffinose, stachyose and verbascose (in beans, peas, lentils, cabbage, whole grains), soybean oligosaccharides in soy, and trans-galactooligosaccharides (TOS),
- Gentio-oligosaccharides (produced from pustulan)
- Gluco-oligosaccharides (produced from sucrose)
- Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO) (human breast milk)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides or IOS (produced from starch)
- Lactosucrose (produced from lactose and sucrose)
- Maltotriose (produced from starch during digestion, found in liquid glucose, brown rice syrup)
- Mannan-oligosaccharides or MOS (artificially produced)
- Melibiose-derived oligosaccharides
- N-acetylchito-oligosaccharides (derived from chitosan)
- Pectic oligosaccharides (derived from pectin)
- Xylo-oligosaccharides (produced from corncob and birch wood)
Oligosaccharides are often added to commercial foods as sweeteners or fiber.
Digestion, Fermentation, Absorption, Function, Side Effects
Oligosaccharides, except maltotriose, are indigestible, which means humans lack enzymes to break them down in the small intestine, so they reach the large intestine, where beneficial colonic bacteria break them down (ferment) to absorbable nutrients, which provide some energy–about 2 Calories (kilocalories) per gram in average [1]. Certain breakdown products of oligosaccharides–namely short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)–may have beneficial effect on large intestinal lining.
Most oligosaccharides act as a soluble fiber, which may help prevent constipation. Ingestion of large amount of oligosaccharides can result in abdominal bloating and excessive gas (flatulence).
Oligosaccharides as Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible nutrients that selectively promote the growth of normal intestinal bacteria that may have beneficial effects on the large intestinal lining. Oligosaccharides currently considered as prebiotics include fructooligosaccharides (FOS) or oligofructose and trans-galactooligosaccharides (TOS) [2].
Related Nutrients
Carbohydrates
- Fructose
- Galactose
- Glucose
- Isomaltose
- Isomaltulose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Mannose
- Sucrose
- Tagatose
- Trehalose
- Trehalulose
- Xylose
- Erythritol
- Glycerol
- Hydrogenated starch hydrolysates (HSH)
- Inositol
- Isomalt
- Lactitol
- Maltitol
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides (IMO)
- Maltotriose
- Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS)
- Raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
- SOLUBLE FIBER:
- Acacia (arabic) gum
- Agar-agar
- Algin-alginate
- Arabynoxylan
- Beta-glucan
- Beta mannan
- Carageenan gum
- Carob or locust bean gum
- Fenugreek gum
- Galactomannans
- Gellan gum
- Glucomannan or konjac gum
- Guar gum
- Hemicellulose
- Inulin
- Karaya gum
- Pectin
- Polydextrose
- Psyllium husk mucilage
- Resistant starches
- Tara gum
- Tragacanth gum
- Xanthan gum
- INSOLUBLE FIBER:
- Cellulose
- Chitin and chitosan
- FATTY ACIDS
- Saturated
- Monounsaturated
- Polyunsaturated
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
- Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)
- Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs)
- Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs)
- Monoglycerides
- Diglycerides
- Triglycerides
- Vitamin A - Retinol and retinal
- Vitamin B1 - Thiamine
- Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin
- Vitamin B3 - Niacin
- Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid
- Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxine
- Vitamin B7 - Biotin
- Vitamin B9 - Folic acid
- Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin
- Choline
- Vitamin C - Ascorbic acid
- Vitamin D - Ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol
- Vitamin E - Tocopherol
- Vitamin K - Phylloquinone
- Curcumin
- FLAVONOIDS:
- Anthocyanidins
- Flavanols: Proanthocyanidins
- Flavanones: Hesperidin
- Flavonols: Quercetin
- Flavones: Diosmin, Luteolin
- Isoflavones: daidzein, genistein
- Caffeic acid
- Chlorogenic acid
- Lignans
- Resveratrol
- Tannins
- Tannic acid
- Alcohol chemical and physical properties
- Alcoholic beverages types (beer, wine, spirits)
- Denatured alcohol
- Alcohol absorption, metabolism, elimination
- Alcohol and body temperature
- Alcohol and the skin
- Alcohol, appetite and digestion
- Neurological effects of alcohol
- Alcohol, hormones and neurotransmitters
- Alcohol and pain
- Alcohol, blood pressure, heart disease and stroke
- Women, pregnancy, children and alcohol
- Alcohol tolerance
- Alcohol, blood glucose and diabetes
- Alcohol intolerance, allergy and headache
- Alcohol and psychological disorders
- Alcohol and vitamin, mineral and protein deficiency
- Alcohol-drug interactions

18 Responses to "Oligosaccharides"