Disaccharides
Disaccharides Definition
Disaccharides [Greek di = two; sacchar = sugar] are sugars composed of 2 monosaccharides (Chart 1). Disaccharides, along with monosaccharides, are called simple carbohydrates.
Three Common Disaccharides
The three most common disaccharides in foods are sucrose, lactose and maltose.
A Typical Disaccharide Structure
A disaccharide molecule is formed by 2 monosaccharides, joined by a glycosidic bond (Picture 1). The type of a glycosidic bond can determine the properties of certain disaccharides. For example, sucrose, isomaltulose and trehalulose are all composed of glucose and fructose, which are linked by different types of glycosidic bonds.
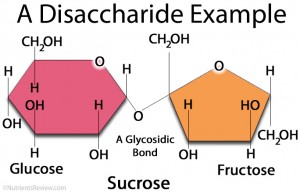
Picture 1. A disaccharide sucrose composed of
monosaccharides glucose and fructose
Disaccharides Examples
Chart 1. Disaccharides list, calorie value, food sources
| DISACCHARIDE | STRUCTURE | ENZYME required for digestion | Kcal/g | FOODS high in disaccharides |
| Sucrose (saccharose, table sugar) | Glucose + fructose | Sucrase | 3.9 | Table sugar, molasses, maple syrup, fondant, cakes, candies, chocolate, ice cream, fruits, honey |
| Lactose (milk sugar) | Glucose + galactose | Lactase | 3.9 | Milk, ice cream, infant formula, milk chocolate, milk candies, certain pills |
| Maltose (malt sugar) | Glucose + glucose | Maltase, isomaltase | 4 | Spelt, kamut, sweet potatoes, barley malt syrup, high maltose corn syrup (HMCS), beer, or produced from corn |
| Isomaltose | Glucose + glucose | Isomaltase, maltase | <2 | Produced during digestion of starch (bread, potatoes, rice…), or artificially produced |
| Isomaltulose | Glucose + fructose | Isomaltase | 4 | Sugar cane syrup, honey, or artificially produced |
| Trehalose | Glucose + glucose | Trehalase | 4 | Mushrooms, honey, seafood, wine, or artificially produced |
| Trehalulose | Glucose + fructose | Isomaltase | 4 | Artificially produced from sucrose |
Function
Disaccharides are an energy source; most of them provide about 4 Calories (kilocalories) per gram, just like other carbohydrates. Disaccharides are non-essential nutrients, which means they are not necessary for health or life of human beings.
Digestion and Absorption
In order to be absorbed, disaccharides need to be digested, that is broken down, by intestinal enzymes into simple sugars (monosaccharides), which are then absorbed in the small intestine.
Disaccharide Intolerance
Disaccharide intolerance refers to gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, bloating) caused by poor digestion of disaccharides due to lack of respected intestinal enzymes. Lactose intolerance is common, but intolerances to other disaccharides are rare.
Similar Nutrients
Carbohydrates
- Fructose
- Galactose
- Glucose
- Isomaltose
- Isomaltulose
- Lactose
- Maltose
- Mannose
- Sucrose
- Tagatose
- Trehalose
- Trehalulose
- Xylose
- Erythritol
- Glycerol
- Hydrogenated starch hydrolysates (HSH)
- Inositol
- Isomalt
- Lactitol
- Maltitol
- Mannitol
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS)
- Galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS)
- Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO)
- Isomalto-oligosaccharides (IMO)
- Maltotriose
- Mannan oligosaccharides (MOS)
- Raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
- SOLUBLE FIBER:
- Acacia (arabic) gum
- Agar-agar
- Algin-alginate
- Arabynoxylan
- Beta-glucan
- Beta mannan
- Carageenan gum
- Carob or locust bean gum
- Fenugreek gum
- Galactomannans
- Gellan gum
- Glucomannan or konjac gum
- Guar gum
- Hemicellulose
- Inulin
- Karaya gum
- Pectin
- Polydextrose
- Psyllium husk mucilage
- Resistant starches
- Tara gum
- Tragacanth gum
- Xanthan gum
- INSOLUBLE FIBER:
- Cellulose
- Chitin and chitosan
- FATTY ACIDS
- Saturated
- Monounsaturated
- Polyunsaturated
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
- Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs)
- Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs)
- Very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs)
- Monoglycerides
- Diglycerides
- Triglycerides
- Vitamin A - Retinol and retinal
- Vitamin B1 - Thiamine
- Vitamin B2 - Riboflavin
- Vitamin B3 - Niacin
- Vitamin B5 - Pantothenic acid
- Vitamin B6 - Pyridoxine
- Vitamin B7 - Biotin
- Vitamin B9 - Folic acid
- Vitamin B12 - Cobalamin
- Choline
- Vitamin C - Ascorbic acid
- Vitamin D - Ergocalciferol and cholecalciferol
- Vitamin E - Tocopherol
- Vitamin K - Phylloquinone
- Curcumin
- FLAVONOIDS:
- Anthocyanidins
- Flavanols: Proanthocyanidins
- Flavanones: Hesperidin
- Flavonols: Quercetin
- Flavones: Diosmin, Luteolin
- Isoflavones: daidzein, genistein
- Caffeic acid
- Chlorogenic acid
- Lignans
- Resveratrol
- Tannins
- Tannic acid
- Alcohol chemical and physical properties
- Alcoholic beverages types (beer, wine, spirits)
- Denatured alcohol
- Alcohol absorption, metabolism, elimination
- Alcohol and body temperature
- Alcohol and the skin
- Alcohol, appetite and digestion
- Neurological effects of alcohol
- Alcohol, hormones and neurotransmitters
- Alcohol and pain
- Alcohol, blood pressure, heart disease and stroke
- Women, pregnancy, children and alcohol
- Alcohol tolerance
- Alcohol, blood glucose and diabetes
- Alcohol intolerance, allergy and headache
- Alcohol and psychological disorders
- Alcohol and vitamin, mineral and protein deficiency
- Alcohol-drug interactions

3 Responses to "Disaccharides"